Sustainability goals and results
Annual Sustainability Goals for Each Material Issues
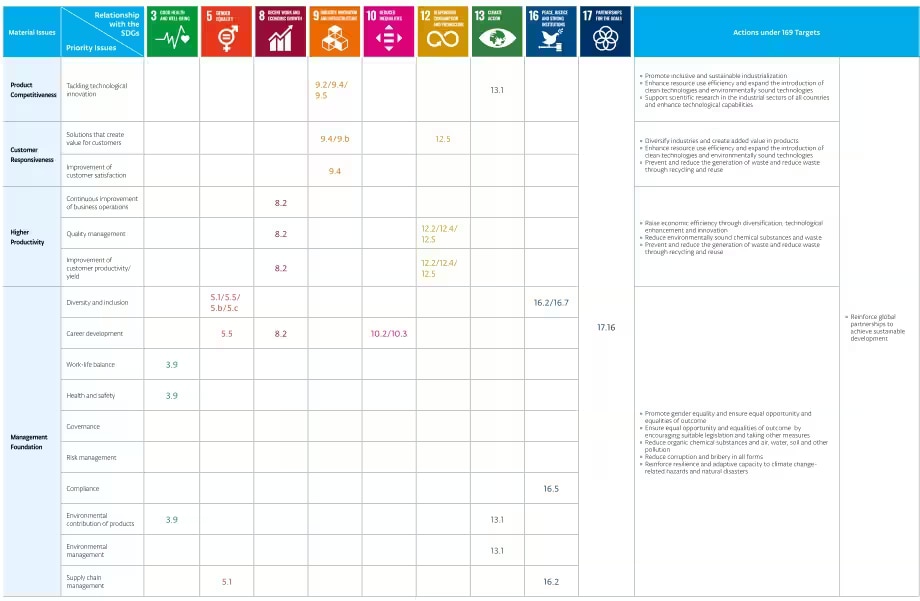
Tokyo Electron is identifying the priority themes for each material issue, setting annual sustainability goals for each fiscal year, and understanding and verifying the progress of results.
We have also clearly identified the persons responsible for each goal, and by conducting various activities to achieve said goals, we are in turn contributing to the SDGs and further enhancing our corporate value.
Annual Sustainability Goals and Results
Goals and Results for Fiscal Year 2023
| Material Issues | Priority Themes | Annual Sustainability Goals | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Competitiveness | Tackling technological innovation |
|
|
|
|
||
| Customer Responsiveness | Solutions that create value for customers |
|
|
|
|
||
| Improvement of customer satisfaction |
|
|
|
| Higher Productivity | Continuous improvement of business operations |
|
|
| Quality Management |
|
|
|
|
Internal audits carried out*⁴ based on Quality Regulations (TEL Manual/TEL Guidelines*⁵)
|
||
| Improvement of customer productivity/yield |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Management Foundation | Diversity and inclusion |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Career development |
|
|
|
| Work-life Balance |
|
|
|
| Health and safety |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Governance |
|
|
|
| Risk Management |
|
|
|
| Compliance |
|
|
|
| Environmental contributions of products |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Environmental management |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Supply Chain Management | Implement supply chain sustainability assessments for the following percentages of suppliers
|
|
|
Implement supply chain BCP*11 assessment for the following percentages of suppliers
|
|
Global patent filing rate: Percentage of inventions filed as a patent application in multiple countries
For each question, average score is calculated for all customers who responded
QA-BOX: Tool for the sharing and horizontal deployment of important quality-related information within our Group companies
Audited sites: Tokyo Electron Technology Solutions Tohoku Office, Tokyo Electron Kyushu, Tokyo Electron Miyagi
TEL Manual/TEL Guidelines: Regulations based on company-wide quality policies set for each major business category, such as development, designed, manufacturing, and services
B-FMEA: Base-Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
Include experts in the number of managers
ERM: Enterprise Risk Management. Refer to Risk Management
Per-unit basis: Calculated using complex weighting of the number of developed evaluation machines, units produced, floor area and labor-hours for each district
Per-unit basis: Calculated based on floor area and labor-hours, etc., for each district
BCP: Business Continuity Plan
Goals for Fiscal Year 2024
| Material Issues | Priority Themes | Annual Sustainability Goals | Initiative to the SDGs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Competitiveness Continuously create high value-added next-generation products |
Tackling technological innovation |
|
|
| Customer Responsiveness Strong relationship based on trust /Sole strategic partner |
Solutions that create value for customers |
|
|
| Improvement of customer satisfaction |
|
||
| Higher Productivity Pursuit of operational efficiency |
Continuous improvement of business operations |
|
|
| Quality Management |
|
||
| Improvement of customer productivity/yield |
|
||
| Management Foundation Build a strong management foundation that underpins our business activities |
Diversity and inclusion |
|
|
| Career development |
|
||
| Work-life Balance |
|
||
| Health and safety |
|
||
| Governance |
|
||
| Risk Management |
|
||
| Compliance |
|
||
| Environmental contribution of products |
|
||
| Environmental management |
|
||
| Supply Chain Management | Supply chain sustainability assessment implementation rate
|
||
Implement supply chain BCP assessment for the following percentages of suppliers
|
Revised listing method for targets
169 Targets of the SDGs